Retrobulbar anaesthesia and Nadbeth block
Retrobular anesthesia is demonstrated in this video. We are using a 10cc syringe filled with 8cc of 2% xylocaine with a 25G 11/2 inch long needle. The patient is directed to look straight ahead and to avoid closing his/her eyes during the injection. The site of injection should be located at the junction of the lateral 1/3 and medial 2/3s of the inferior orbital rim. The globe is palpated and may be gentle elevated to avoid inadvertent ocular penetration. The needle is initially directed posteriorly until penetration of the skin and orbicularis muscle is achieved, at which point the needle is directed toward the apex of the orbit. At this point, the plunger of the syringe is gentle pulled back to ensure that the needle is not located within a blood vessel. The xylocaine is then steadily injected into the orbit. We usually begin with a 3cc volume and reinject if deemed necessary. Pressure is maintained over the injection site and globe to avoid hemorrhage and distribute the anaesthetic within the orbit. Early signs of a successful retrobulbar injection include ptosis and pupillary dilatation. Akinesis and regional analgesic effect occurs within minutes.
Although retrobulbar anaesthesia provides adequate ophthalmoplegia, it may not completely anaesthestize the cornea and conjunctiva. We routinely use 0.5% tetracaine in minim format as our pre- and intraoperative topical anaesthetic.
A Nadbeth block is used to minimized squeezing of the eyelids against the speculum. We routinely inject 3cc of xylocaine from the fossa behind the pinna aiming towards the orbit. This blocks 7th cranial nerve function and therefore relaxes the orbicularis oculi muscles. We used the same syringe as the retrobulbar, but exchange the needle for a 25G 5/8 inch.
At this point, if we deem it necessary, we may inject a further 1-2 cc of xylocaine in the retrobulbar space as described above. In this case, after the second injection we achieve a relatively complete ophthalmoplegia of the right eye.
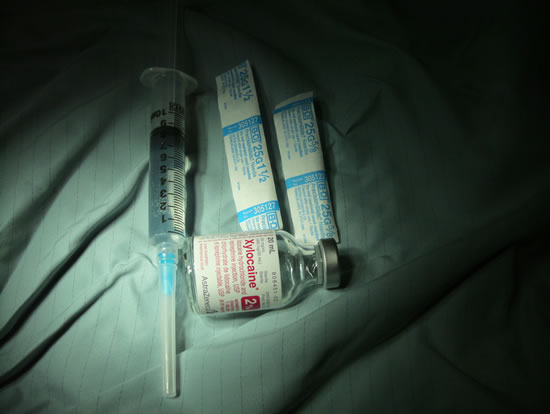
This photo demonstrates the necessary supplies for retrobulbar anaesthesia. These include xylocaine 2% with epinephrine, a 10cc syringe, a 25G 1 ½ inch needle and a 25G 5/8 needle. Typically we fill the syringe with 8cc of xylocaine 2% with epinephrine.
