The students in the lab will NOT perform this experiment. It will be set-up for you beforehand as a demonstration and the results are to be observed at the Central Bench, 1h after it has been set-up.
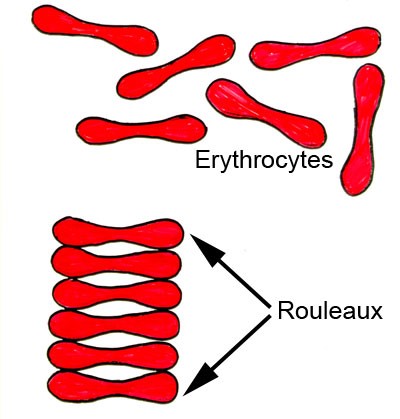
RBCs sediment because their density is greater than that of plasma; especially when there is an alteration in the distribution of charges on the surface of the RBC (which normally keeps them separate from each other) resulting in their coming together to form large aggregates known as rouleaux.
Rouleaux formation is determined by increased levels of plasma fibrinogen and globulins, and so the ESR reflects changes in the plasma proteins that accompany acute and chronic infections, some tumors and degenerative diseases. In such situations, the ESR values are much greater than 20 mm/hr.
Note that the ESR denotes only the presence of tissue damage or disease, but not its severity; it may be used to follow the progress of the diseased state, or monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Some interferences which increase ESR:
- increased level of fibrinogen, gamma globulins.
- technical factors: tilted ESR tube, high room temperature.
- abnormally shaped RBC (sickle cells, spherocytosis).
- technical factors: short ESR tubes, low room temperature, delay in test performance (>2 hours), clotted blood sample, excess anticoagulant, bubbles in tube.
- Chronic inflammatory disease (collagen and vascular diseases) increases ESR.
- Polycythemia decreases ESR.
- Polycythemia decreases ESR.


