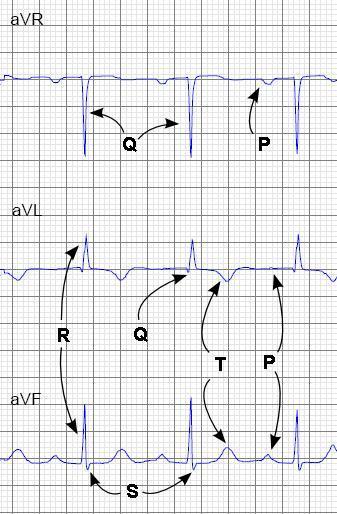
Normal sinus rhythm means a regular rhythm generated by the SA node. The parts of a normal EKG waveform are probably familiar to you and we review it here only briefly in the picture below.

Other simple things to note about a standard EKG tracing are:
This means that if you saw a strange event like a premature beat in lead V1, it should appear in V2 and V3, but not in the other leads. This is clear in the tracing below.
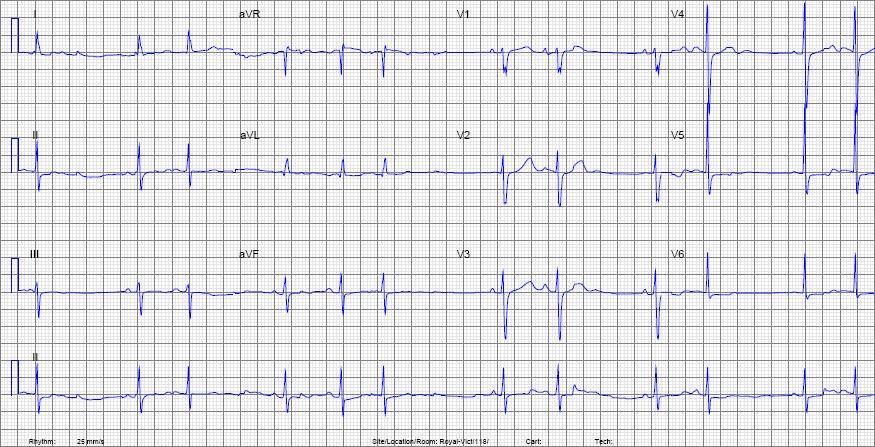
For practice, calculate the rate for the above EKG.
| Rate | about 72 |
We also want to see that the P-waves are actually coming from the SA node - which is located in the right atrium up toward the patient's right shoulder. So we expect the P-waves to be going away from the right shoulder (downward, and from right to left). On the EKG this means the P-waves should be positive in leads I and II as shown below.
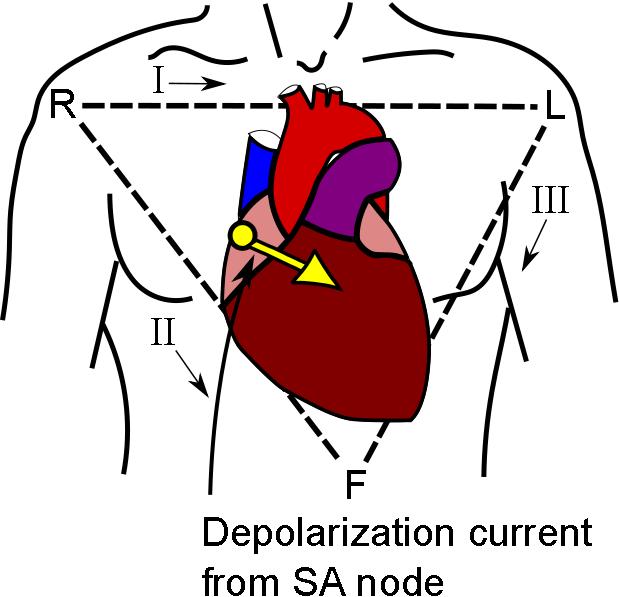
So our second way of identifying normal sinus rythym is:
And finally, we don't want any blocks in conduction, so:
And now try to analyse the example below. Get the rate and decide whether this is normal sinus rhythm or not.
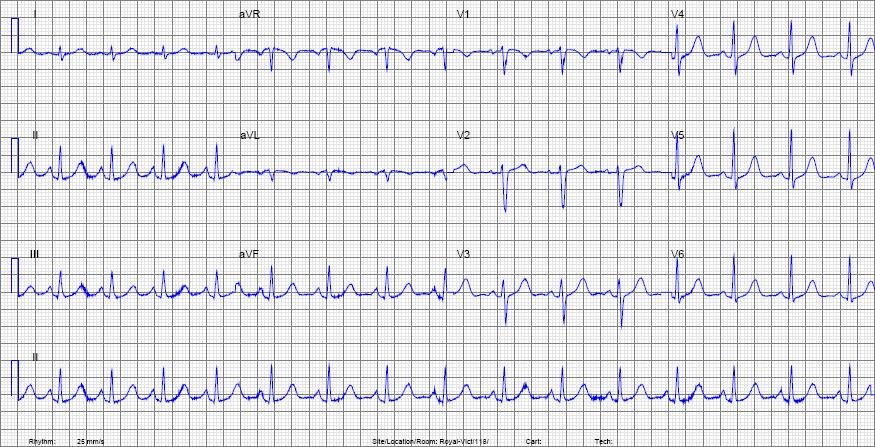
| Rate | about 100 |
| Rhythm | Normal sinus rhythm. There is a P-waves before each QRS, the P-waves are negative in aVR and positive in II and the rhythm is regular. |