Chapter 22 - The Epididymis
B Robaire, BT Hinton, MC Orgebin-Crist
Plates (1st Edition)
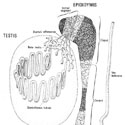
Fig. 1
Diagrammatic representation of the testis showing a seminiferous tubule and the rete testis, the ductuli efferentes, the epididymis and vas deferens. The shaded regions indicate areas of the different segments of the epididymis, i.e., the initial segment, caput, corpus, and proximal and distal cauda, where data on the relative quantitative distribution of the major different epithelial cell types were obtained.
Fig. 2
Light microscope photograph showing the sharp demarcation between the cuboidal epithelial cells of the rete testis (RT) and the columna epithelial cells of the efferent ducts (ED)
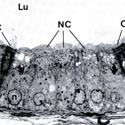
Fig. 3
Portion of the epithelium from the initial zone of an efferent duct at the light microscopic level showing numerous nonciliated cells (NC) and few ciliated cells (C)
Fig. 4
Portion of the epithelium from the terminal zone of an efferent duct showing nonciliated (NC) and ciliated (C) cells
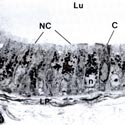
Fig. 5
Light microscope photograph showing several tubules of the initial segment of the epididymis
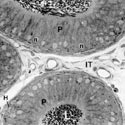
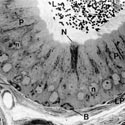
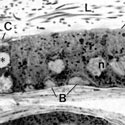
Fig. 6
Portion of the epithelium lining the initial segment of the epididymis illustrating many tall columnar principal cells (P) with pale, round nuclei (n) located at different levels of the cell and showing a prominent nucleolus, a few elongated basal cells (B) at the base of the epithelium, and a deeply stained narrow cell (N). Longitudinal dense bands extend along the length of principal cells (arrowheads)
Fig. 7
Epithelium lining the epididymal duct of the caput epididymidis showing numerous principal cells (P) and a few clear cells (C)
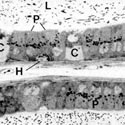
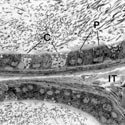
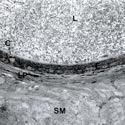
Fig. 8
Principal (P) and clear (C) epithelial cells lining the caput epididymidis
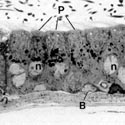
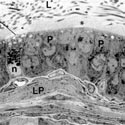
Fig. 9
Epithelium lining the epididymal duct of the corpus epididymidis showing numerous principal (P) cells and a clear (C) cell
Fig. 10
Principal (P) and clear (C) epithelial cells lining the corpus epididymidis.
Fig. 11
Epithelium lining the epididymal duct of the cauda epididymidis showing principal (P) and clear (C) cells
Fig. 12
Principal (P) and clear (C) epithelial cells lining the cauda epididymidis
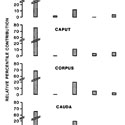
Fig. 13
Relative cell distribution in the initial segment, caput, corpus, and cauda epididymidis of the adult male rat
Fig. 14
Portion of the epithelium (E) lining the proximal segment of the vas deferens showing many cuboidal principal cells and a clear cell (C)
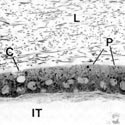
Fig. 15
Epithelium of the proximal segment of the vas deferens lined by cuboidal principal (P) cells and flattened basal (B) cells