|
Blood
Laboratory |
Blood cell indices >
Hematocrit |
| |
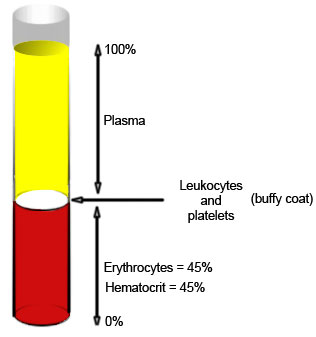
When heparinized blood
(heparin is an anticoagulant) is
centrifuged, the red blood cells become
packed at the bottom of the tube, while
the plasma is left at the top as a clear
liquid. The ratio of the volume of packed
red cells to the total blood volume is
called the hematocrit. |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
Heparinized blood is
transferred from the microcentrifuge tube (often called eppendorf tube) to a microhematocrit
capillary. The
tube is filled to at about 3/4 capacity
by capillary action. |
|
Then the
blood-filled end is sealed with clay, and
placed in a slot in the hematocrit
centrifuge. |
 |
|
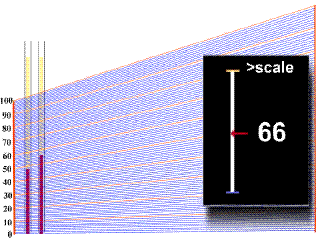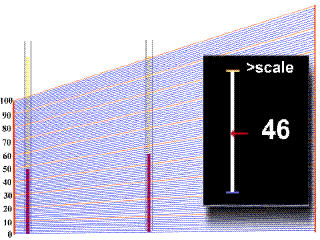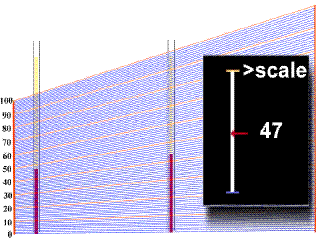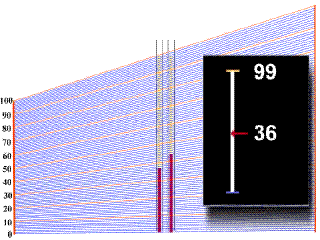
In order to obtain a value of
hematocrit from the centrifuged blood sample in
the capillary tube, one must refer to a
scale
plate, which is located directly under the
samples in the centrifuge. The bottom of the
packed red cell column is first lined up with the
"0" line on the scale plate, and then
the scale is moved under the sample until the top
of the plasma column lines up with
the"100%" line. In the example animation
given below, watch as first one, and then a
second sample tube moves over the grid. A black
square on the right will give you a digital
reading at a given point, but make sure that you
note the right one! |
 |
 |
|
|
- You should
have obtained a value of 44% for the
first tube, and 37% for the second tube.
- Note that the
normal range of values for hematocrit are
as follows:
| Female: |
36-48% |
| Male: |
40-52% |
|
|
To
continue to the next section Hemoglobin content determination, click here |