|
Blood
Laboratory |
Blood typing |
| |
The blood groups
refer to the presence on human red blood cells of
certain antigens, the blood group factors. One
very important group of factors present on the
red blood cells is the ABO system. The ABO group
of a person depends on whether his/her red blood
cells contain one, both, or neither of the 2
blood group antigens A and B. There are,
therefore, 4 main ABO groups: A, B, AB and O. |
|
Antibodies (agglutinins) for the antigens A and B exist in the
plasma and these are termed anti-A and anti-B. The corresponding
antigen and antibody are never found in the same individual since, when
mixed, they form antigen-antibody complexes, effectively agglutinating
the blood. |
|
Testing for ABO Group -
Procedure |
|
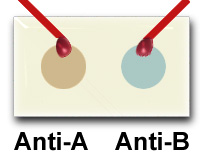
One end
of a slide is labelled Anti-A, and the
other Anti-B. A drop of Anti-A test serum
is added to the end marked Anti-A, and a
drop of Anti-B serum is added to the end
marked Anti-B. |
 |
|
One drop
of blood is added to each end of the
slide, and mixed well, using separate
wooden sticks. |
 |
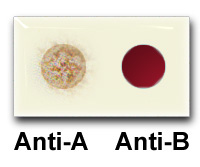
| The
results are read directly from the slide.
The subject is blood group A if
agglutination occurred with the Anti-A
test serum; group B if agglutination
occurred with the Anti-B test serum;
group AB if agglutination occurred with
both test serums, and O if there was no
agglutination in either case.
In the
sample to the right, we conclude the
subject has type A blood. |
 |
|
Examine the slides below and determine the
blood type of the subject in each case. Click below to check your
answer. |
|
1 |
 |
 |
2 |
|
3 |
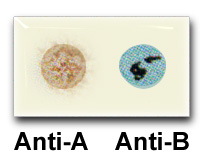 |
 |
4 |
|
|
What is the answer? |
|
When transfusing blood, it is important
to remember that the donor's blood must not contain red blood cells that
the recipient's antibodies can agglutinate. Theoretically, then,
individuals belonging to blood group O are universal donors, while those
of blood group AB are universal recipients. |
|
The
Rh System |
Rh
antigens, named for the rhesus monkey in which they were first
discovered, are also surface antigens expressed on red blood cells.
There are a few Rh antigens (common one is called D). Red cells
expressing the Rh antigens are called Rh positive. Red cells which do
not express this surface antigen are Rh negative (about 15% of the human
population is Rh negative).
Rh system becomes important when one considers the eventuality of Rh
incompatibility between mother and fetus; in such a case, the
antibody-mediated cytotoxicity mechanism involved threatens the
well-being of the fetus.
During birth, a leakage of the baby's red blood cells often occurs into
the mother's circulation. If the baby is Rh positive (inheriting the
trait from its father) and the mother is Rh negative, these red cells
will cause the mother to manufacture antibodies against the Rh antigen.
The antibodies (IgG class) do not cause problems for that first born,
but can cross the placenta and attack the red cells of a subsequent Rh+
fetus. The red cells are destroyed, leading to anemia and jaundice. The
disease - erythroblastosis fetalis or hemolytic disease of the newborn-
may result in fetal death. |
|
|
|
Click here to return to the Virtual lab home
page |