|
Compound Action Potential |
Characteristics of the CAP |
| |
The objective of this part of the lab is to record the
Compound Action Potential, and to observe and measure its general characteristics,
including its latency, threshold, shape, and their dependence on stimulus strength. |
|
|
|
|
The parameters on the stimulator
are set as shown to the left. Note that setting the stimulator mode to
"Repeat" initiates repetitive stimulation, in this case at a rate of 1Hz (once
per second). |
| Stimulator
Settings |
|
Stimulus Duration:
0.2 ms |
| Stimulus Voltage: 0.05 V |
| Delay: 1 ms |
| Rate: 1 Hz |
| Mode: Repeat |
|
|
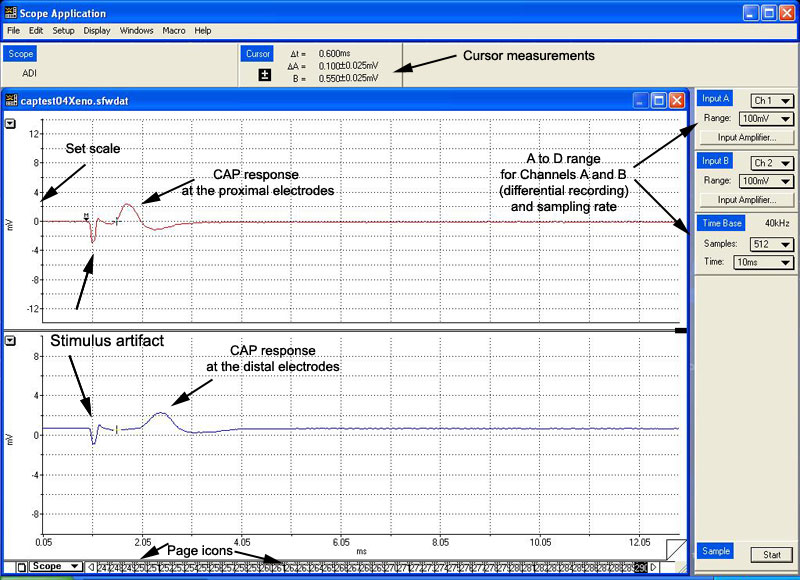
A sample display might look
something like what you see to the right below. The Compound Action Potential is the
second biphasic waveform, the Stimulus Artifact (explained below) appears first. It
is important not to confuse the two! |
|
Note the Input Channels A and B ranges. By setting the A
to D range, you change the A to D(hardware) gain, in order to more accurately view
the CAP signal. |
 |
|
|
|
Changes in CAP with
increasing stimulus amplitude |
|
|
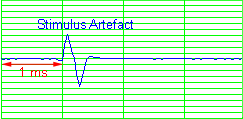
With a low initial stimulus
amplitude, no CAP will be visible, but you will see a brief, biphasic deflection near the
beginning of the display. This is the stimulus artifact, which results from
virtually instantaneous, passive current spread from stimulating electrodes to recording
electrodes. |
|
The delay dial on the stimulator is adjusted so that
the stimulus artifact begins exactly 1 ms from the start of the sweep. |
|
|
As we slowly increase the stimulus voltage,
using the control knob on the stimulator, at a certain point a second deflection will
appear in the displayed waveform. This is the Compound Action Potential of the
nerve. As we increase stimulus voltage further, observe the corresponding changes in the
CAP shape and amplitude. |
|

|
|
The following CAP
characteristics are read from the computer display: |
|
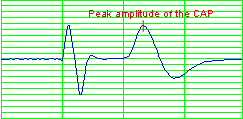
The peak amplitude of
the CAP is the voltage value of the peak of the CAP response. |
|
|
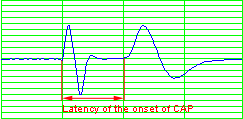
The latency of the onset
of the CAP is the time from the onset of the stimulus
artifact to the onset of the
CAP.
|
|
|
The latency
of the peak of the CAP is the time from the onset of the stimulus
artifact to the
peak of the CAP. |

|
|
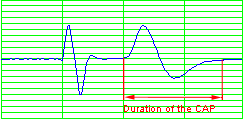
The duration of the CAP
is the time from the the beginning of the positive phase to the end of the negative phase
of the CAP. |
|
|
The following two CAP
characteristics are read from the stimulator box: |
|
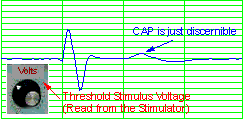
The threshold stimulus
voltage is determined by raising and lowering the stimulus voltage a little to find
the voltage at which the CAP is just discernible. |
|
|
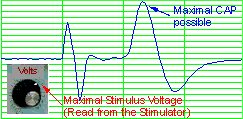
The maximal stimulus
voltage is the point at which a further increase in stimulus voltage produces no
further increase in the CAP amplitude. |
|
|
|
|
Q: Why does the CAP increase
in size and duration with increasing stimulus strength?
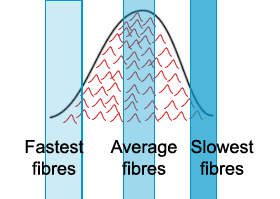
A: The CAP is the algebraic sum of all individual
fibre
action potentials of the nerve. As stimulus strength increases, we recruit more
fibres, therefore more APs add up to produce a larger bell-shaped curve. Recall that
the conduction velocity of single fibres depends on fibre diameter, and that the nerve
bundle is composed of fibres of varying diameter. Fast fibres (large diameter, low
threshold) will contribute APs that fall towards the start of the CAP, slower
fibres
(small diameter, high threshold) will contribute APs that fall towards the tail section.
As we gradually increase stimulus strength, we recruit more and more
fibres giving
rise to a wider CAP, with longer duration. |
|
Q:
What is the significance of measuring the latency to the beginning of the CAP, versus
measuring it to the peak of the CAP?
A: The latency of the beginning of the CAP reflects how long it
takes for the fastest fibres to conduct action potentials from the stimulus source to the
recording electrodes. When the latency is measured to the peak of the CAP, we obtain
the latency of an average fibre in the nerve. |
Q: What is the significance of the threshold voltage?
A: The threshold voltage, measured from the stimulator, is the
voltage needed to generate at least one AP from a fibre in the sciatic nerve bundle.
(Remember when we speak of CAP thresholds, we are dealing with a whole nerve and
not an individual fibre.) As the resolution of the screen is poor, it is hard to measure
an accurate threshold. The true thresholds are in reality much lower. |
Q: What happens when we
increase stimulus voltage beyond maximal?
A: The size of the CAP no longer increases, because all of the
A-alpha fibres making up the nerve have been excited and are conducting action potentials.
Note: Not
all nerve fibers have actually been recruited at this
point, for as you will see in the conduction velocity part of the experiment, with even
higher stimulus strengths we will be able to recruit a distinct secondary group of much
slower fibres of the nerve (the A-beta fibres). |
|
Click here to continue with the
topic of Strength-Duration curve |