|
Exercise Physiology Laboratory |
Background Information |
| |
You have learned about the interaction between the
cardiovascular and respiratory systems during the lectures, and
you are familiar with the measurements of respiratory and
cardiovascular variables that you have recorded in the previous
laboratories. You are also familiar with the theory of exercise
physiology, working muscles and production of energy and oxygen
consumption.
|
|
As you know, the
respiratory system is responsible for gas exchange: the delivery
of O2 from the atmosphere to the lungs and the
removal of CO2 produced by the body to the
atmosphere. The cardiovascular system is responsible for the
delivery of O2 to all tissues of our body and the
removal of CO2 from the tissues, and bringing CO2
back to the lungs. Therefore, in the maintenance of homeostasis,
one system depends on the other. You also remember that the
amount of O2 used and CO2 produced depend
on the body metabolic rate, and that metabolic rate increases
during exercise. |
|
|
|
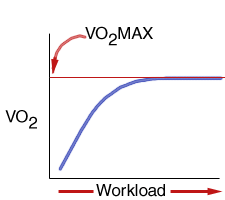
Oxygen uptake (VO2)
increases in proportion to the increase in the exercise level,
workload. More energy per unit time (power) is required to
perform a heavier workload. Therefore, at greater workloads VO2
increases proportionately. However, above a certain level of
workload, VO2 remains constant: VO2
reached its maximum. As you already know, this level of VO2
is called VO2MAX. |
|
 |
|
There are some
factors that have to be considered in determining VO2
MAX:
Posture should
be upright. Horizontal position may decrease VO2
MAX by 30%.
Muscle mass
used in the exercise. Large muscles must be used. About 50% of
the total muscle mass must be engaged in exercise before VO2
MAX can be achieved.
Exercise
duration. Both exercise duration and intensity must be great
enough to elicit near maximal response of the cardiovascular
system. A minimum of 3-4 min is required for each level of
exercise, and the level of workload is increased
progressively.
Prediction of
Maximum Oxygen Uptake
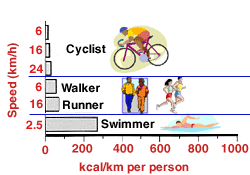
VO2 MAX
is exercise specific.VO2 MAX measured using an
ergometer will be specific for cycling, which yields a lower
value than running or cross-country skiing.
|
|
 |
|
Therefore,
this method will underestimate the VO2
MAX by about 5-10%, both because of the muscle pain factor and
the relatively small amount of muscle tissue involved in
bicycling (upper body muscles not used much).
In this laboratory
you will not make a direct measurement of VO2 MAX,
which involves breathing through a 2-way-valve system and use of
gas analyzer, but rather the value will be predicted from the
measurements of your heart rate at different levels of workload.
This method is frequently used since it has been established
that heart rate increases in proportion to workload. |
|
To continue with the next section:
Cardio/CNS contribution, click here |